
- Privacy Policy & Terms
- …
- Privacy Policy & Terms
- Privacy Policy & Terms
- …
- Privacy Policy & Terms
Why Drink Tea?
It is said that
Tea is the second most widely consumed beverage in the world throughout history,
After water.
In fact,
The addition of a mere 1% , 2%, or 3% of dry tea leaves to water
Transforms and enobles it
In such elegant manner,
Like few other ingredients can.
What is in a tea leaf,
That gives it such heavenly
Aroma and taste
To delight our senses
While nourishing body?
What is in a tea leaf,
That allows it
To do so much?
Summary of Bioactive Components in Tea Leaves
Tea leaves contains the following 7 main categories of bioactive compounds
[Please note that some elements, compounds, and their metabolites may cross over multiple categories] :
- Alkaloids
- Amino Acids
- Minerals, especially essential trace mineral
- Pigments
- Polyphenols
- Polysaccharides
- Saponins
- Other elements and compounds yet to be identified
- Cultivation methods and growing environments determine the quality and the quantity of each of of these bioactive compounds that are built into the tea leaves. This is the work of the tea farmer.
- Processing techniques cause dynamic changes in these bioactive compounds. Each step in the process seek to transform, stabilize, and preserve the nutrients in the leaves so that they maybe stored and transported safely. This is the work of the tea master.
- Brewing parameters determine the type and amount of nutrients extracted into your cup of tea. This is the work of tea drinkers.
Before the tea plant was discovered and cultivated,
It grew on its own in the wild.
After tea is consumed,
Its nutrients are digested and transported
Through our digestive and circulatory systems
To repair and maintain our organs.
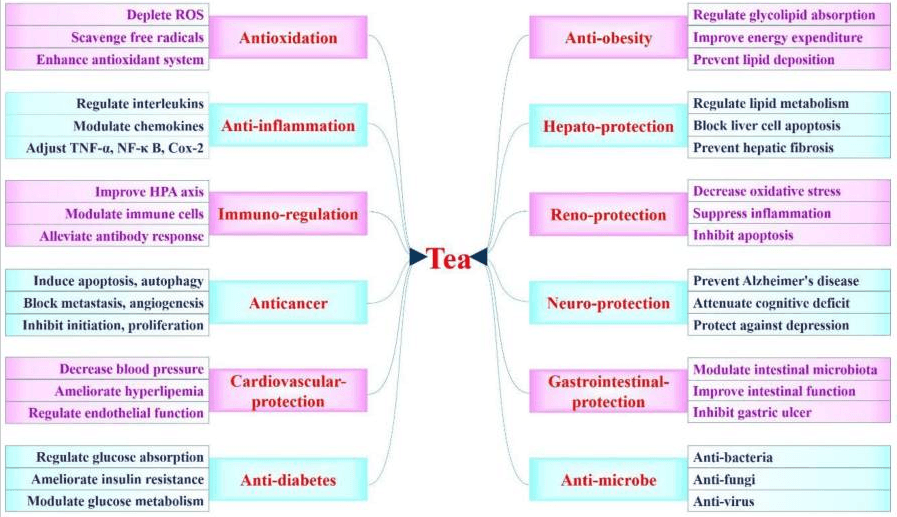
Health Functions Attributed to Consumption of Tea by Humans
Guide to Choosing Tea
- All good tea contain bioactive elements and compounds belonging in the 7 categories described above, in varying amounts. Choosing a tea is only a matter of what you feel like drinking at any particular moment. [green sticker here]
- Through natural cross-breeding, we now have in our collection 2 teas that contain - above and beyond all the other elements and compounds found in all good teas [green sticker here] - a significantly high amount of of a bioactive element that is not found in other tea. These teas are marked with this symbol [hot pink sticker here]. Our Natural Sencha Benefuuki and Natural Sencha Sun Rouge are in this category.
- Caffeine is an alkaloid that gives tea its refreshing quality. Though caffeine in tea enhances mental alertness and ability to focus, it can keep some sensitive people up at night if tea is taken close to bedtime. If you require a tea that provides the health benefits of a good tea [green sticker here] but are sensitive to caffeine, choose a tea that only has just a whisper of caffeine, just enough to lift it out of blandness, but let you sleep soundly at night. These are marked with this symblol [lavender sticker here]. Our Wildcrafted Chaka Tea Blossom, Organic Hojicha, and Organic Chumusi Bancha Yabukita are low caffeine options.
Let the sticker guide your decision:
Green Sticker: All the goodness of an exquisite artisanal tea
Hot Pink Sticker: Focused special benefits above and beyond all the goodness of an exquisite artisanal tea
Lavender sticker: Low Caffeine with all the goodness of an exquisite artisanal tea
Should you need our assistance
In choosing the right tea,
Don't hesitate to contact us:
[link to contact us here]
We are always happy to talk tea with you.
Guide to Brewing tea
Brew hot, or brew cold,
Sip hot, or sip cold,
Whichever way suits you,
Just be bold,
And do it!
Should you need our assistance
With your brewing decision,
Don't hesitate to contact us:
support@chevivo.com
We are always happy to talk tea with you.

Selected References
Green Tea (Camellia sinensis): A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Toxicology https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9231383/#:~:text=The%20alkaloids%20in%20tea%20are,effect%20of%20tea%20%5B22%5D.
Health Functions and Related Molecular Mechanisms of Tea Components: An Update Review.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6941079/pdf/ijms-20-06196.pdf
Tea as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds in the Human Diet https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7967157/#:~:text=Significant%20components%20of%20tea%20also,25%2C26%2C27%5D.
Tea Polyphenols in Promotion of Human Health https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6356332/#:~:text=Polyphenols%20are%20the%20major%20active,epicatechin%2C%20gallocatechins%20and%20gallocatechin%20gallate.
Dietary Effects of Anthocyanins in Human Health: A Comprehensive Review
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8308553/
Bioavailability enhancement of EGCG by structural modification and nano-delivery: A review https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464619306565
Dynamic change in amino acids, catechins, alkaloids, and gallic acid in six types of tea processed from the same batch of fresh tea (Camellia sinensis L.) leaves
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0889157518309207
Therapeutic Effects of Saponins for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer by Ameliorating Inflammation and Angiogenesis and Inducing Antioxidant and Apoptotic Effects in Human Cells
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9504392/
Saponins: A concise review on food related aspects, applications and health implications
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772753X23000114
Oral administration of tea saponins to relive oxidative stress and immune suppression in chickens https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7107189/
Tea Polysaccharides and Their Bioactivities
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6274327/
Polysaccharides from green and black teas and their protective effect against murine sepsis https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996912004759
A comprehensive review on polysaccharide conjugates derived from tea leaves: Composition, structure, function and application https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924224421003423
Advances in the Utilization of Tea Polysaccharides: Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Health Benefits




